This physiological response serves no useful purpose in our current lifestyles. Aside from telling us that we should have packed a coat, modern mammals continue to exhibit this inherent tendency. For example, when faced with cold weather. You may have seen a pigeon puff up on a cold winter day, stretching out its feathers to be warm. If that’s not evidence of evolution, what is?
Furthermore, when an animal feels threatened, such as when you startle a cat, their fur puffs out. This defense mechanism is an old adaptation designed to deceive potential attackers by creating the illusion of increased size.
However, there is one characteristic that unequivocally demonstrates signs of evolution.
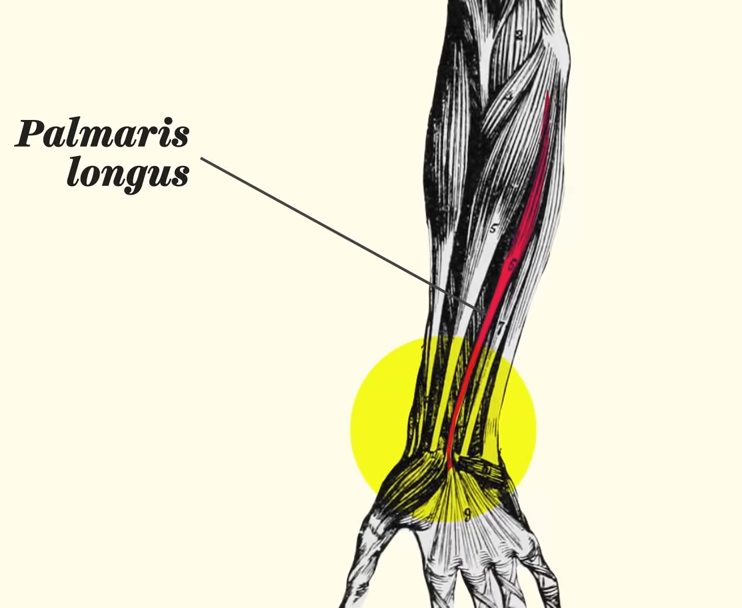
One particularly astounding piece of evolutionary evidence is found in our arms, notably our tendons. A tendon has been evolutionarily phased out in over 10-15% of the human population, indicating that we are still far from the end of evolution.
This tendon is linked to an ancient muscle called the palmaris longus, which was primarily employed by arboreal primates like lemurs and monkeys to move from branch to branch. As humans and ground-dwelling apes, such as gorillas, no longer rely on this muscle or tendon, both species have gradually lost internal function.
